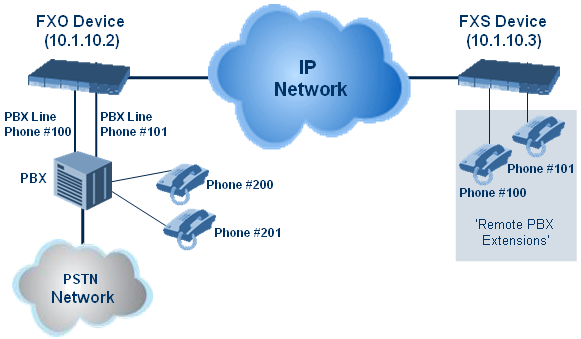
Remote PBX Extension between FXO and FXS Devices
Remote PBX extension offers a company the capability of extending the "power" of its local PBX by allowing remote phones (remote offices) to connect to the company's PBX over the IP network (instead of via PSTN). This is as if the remote office is located in the head office (where the PBX is installed). PBX extensions are connected through FXO ports to the IP network, instead of being connected to individual telephone stations. At the remote office, FXS units connect analog phones to the same IP network. To produce full transparency, each FXO port is mapped to an FXS port (i.e., one-to-one mapping). This allows individual extensions to be extended to remote locations. To call a remote office worker, a PBX user or a PSTN caller simply dials the PBX extension that is mapped to the remote FXS port.
This section provides an example on how to implement a remote telephone extension through the IP network, using FXO and FXS interfaces. In this configuration, the FXO device routes calls received from the PBX to the ‘Remote PBX Extension’ connected to the FXS device. The routing is transparent as if the telephone connected to the FXS device is directly connected to the PBX.
The following is required:
|
■
|
FXO interfaces with ports connected directly to the PBX lines (shown in the figure below) |
|
■
|
FXS interfaces for the 'remote PBX extension' |
|
■
|
PBX (one or more PBX loop start lines) |